
Every year, new methods promising to boost endurance or running performance emerge. Most of them involve expensive supplements or specialized gear. However, one approach remains free and accessible to everyone: low carb running. In this article, we explore how it affects the human body, its potential benefits, and how to use it safely
Tabel of content
1. Short introduction
What is low carb running?
Low carb running is a relatively new approach to running training and nutrition. Most traditional nutrition running plans are carbohydrate-based, recommending an intake of 5-12 gram of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight.
In contrast, train low strategies focus on reducing carbohydrate availibility. These modern strategies limit carbohydrate intake and glycogen level to achieve certain advantages.
In this article, I will use the terms ,,low carb running” and
,,train low running” interchangeably.
Why do runners love carbohydrates?
It’s no coincidence that running experts recommend high carbohydrate diets. The human body prefers glucose as its primary source of energy. It is easier to convert into energy than fats.
However, glucose is less energy dense. A single fat molecule provides more energy than a glucose molecule.
Most runners rely on two forms of carbohydrates as their main fuel source. The first is glucose which we get from foods as fruit, bread, pasta or potatoe. After digestion, body uses it for immediate needs. Excess glucose is converted into glycogen – a long chain of glucose molecules, that acts as energy store.
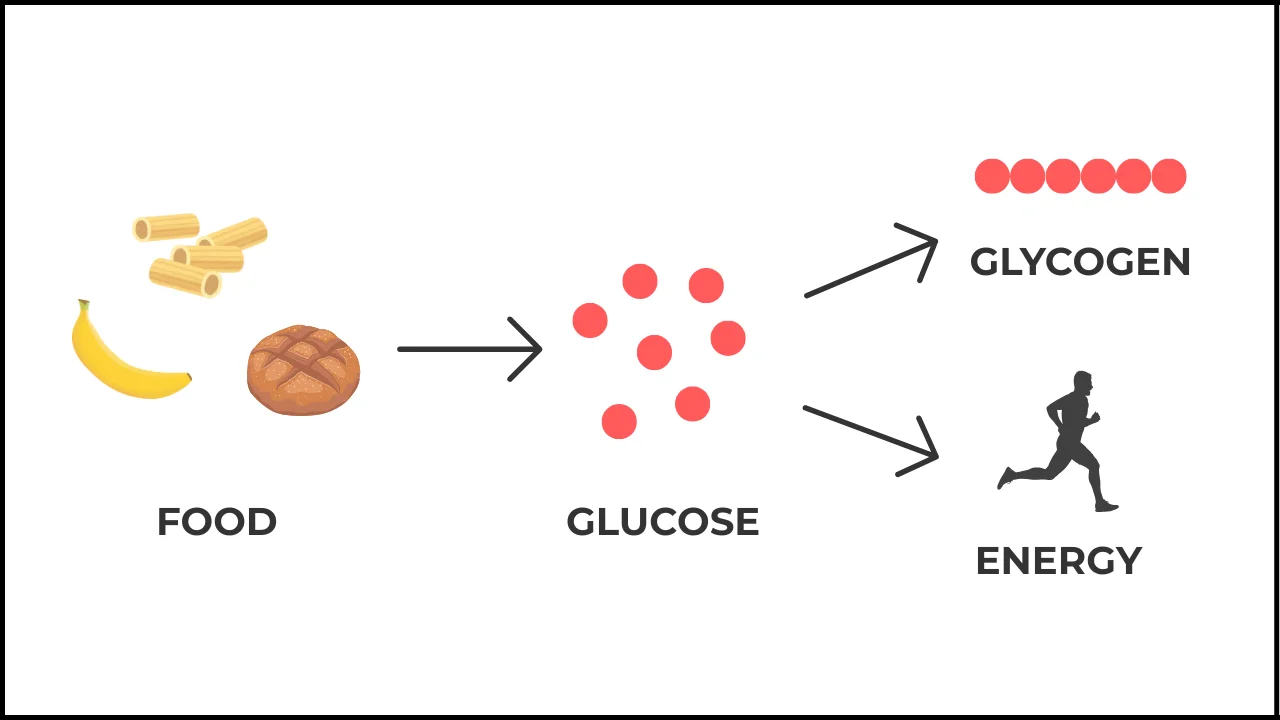
Our ability to store glycogen is limited. Depending on the individual, we can store around 80-120 grams in the liver and 300-500 grams in the muscles. Professional athletes can store up to 700g in muscles.
When we don’t eat for extended period or train intensly, the body starts to use glycogen. High carbohydrate diets help maintain full glycogen stores and a steady glucose supply.
What are the types of low carb running?
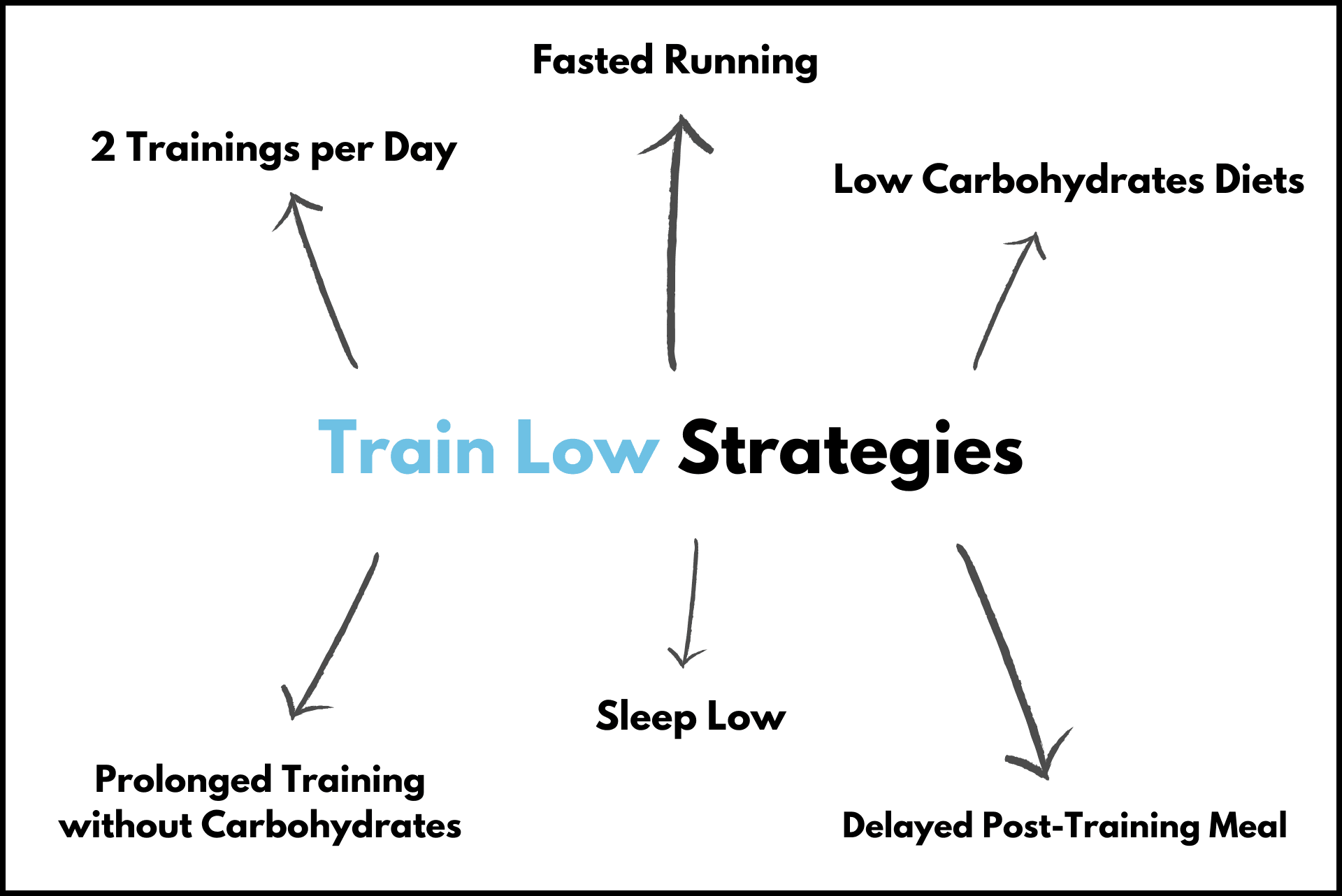
There is no single approach to low carb running. We can achieve low carbohydrate availibility by modifying diet, training time or the way we train.
The most common method is to switch to low carb diets. These diets usually restirct carbohydrate intake to 5-30 % of total energy consumption, forcing body to rely more on fat and protein for energy production.
The next category of train low strategies focuses on training time. The first one is called sleep low, where runner trains intensively in the evening to deplete glycogen stores. It also begins an overnight fast with the end of training. Another popular strategy is training in a fasted state. It is especially popular among early birds.
The final category changes the way we train. Instead of spacing workouts evenly, runners may train twice a day or extend training sessions without carbohydrate intake.
Professional athletes often performe two to three training session per day. Short recovery period, don’t allow the body to fully restore glycogen levels.
Short introduction - Summary
Low-carb running („train low”) is a modern approach to training and nutrition that intentionally limits the availability of carbohydrates in the body.
The human body prefers glucose as its primary fuel because it is easier to convert into energy than fats.
Excess glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, but these reserves are limited.
High-carbohydrate diets help runners maintain full glycogen stores and a steady glucose supply.
There are different train low strategies, which can be achieved through:
Diet: Switching to a low-carb diet (5-30% of energy from carbs)
Training time: Using tactics like „sleep low” or training in a fasted state
Training method: Performing two or more training sessions per day with short recovery periods
2. How train low affects body
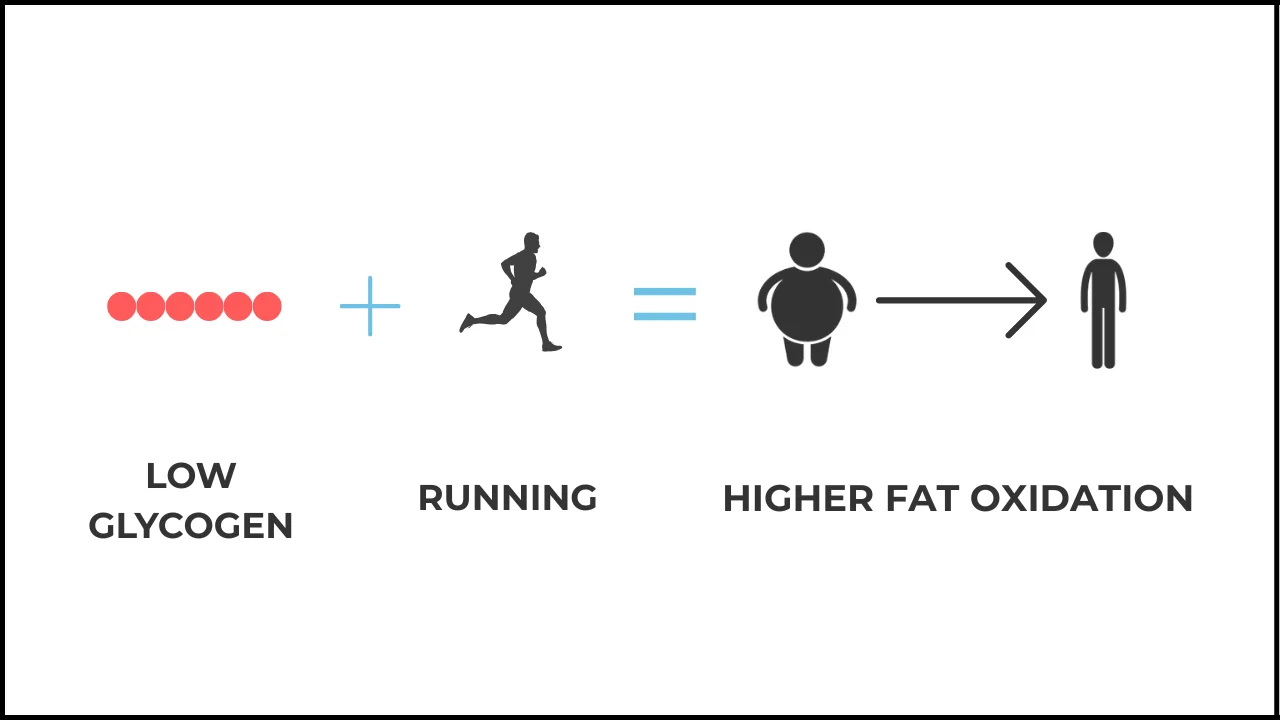
Low carb Running = higher fat oxidation
Low carbohydrate availability trigger a range of metabolic processes. Glycogen depletion forces body to shift from carbohydrate to fats for energy production.
During low carb running, the activity of HAD, an enzyme responsible for fat oxidation, increases. Scientists found that 2 training sessions per day boost activity of HAD by 47% compared to one trening session.
This metabolic flexibility can be especially beneficial in ultra running. During long-distance runs storage of glycogen is limited and access to carbohydrates is reduced. As a result, ultra marathoners rely more on fat as a energy source than others runners.
More mitochondria
Low glycogen level signal body that energy level is low. In response activity of AMPK increases. This essential enzyme plays crucial role in aging prevention, training adaptation and autophagy.
Higher AMPK activity stimulates PGC-1a. This chain of reactions accelerate mitochondrial biogenessis – creation of new mitochondria. The more mitochondria the body has, the more energy it can generate.
Aging is partly linked to the decline in mitochondria number and activity. Training with low glycogen can prepare body for future energy shortages.
Furthermore, scientists found that train low running increases activity of citrate synthase. Runner who train twice a day, exhibit about 34% higher citrate synthase activity compared to those who train once a day.
In sport medicine citrate synthase acts as mitochondrial density marker. It is another sign that low carb running enhances mitochondrial efficiency.
Does Low Carb Running help with metabolic disorders?
One of the most common diseases today is type 2 diabetes. International Diabetes Federation estimates that in 2024 around 588 mln people live with diabetes. Most of them suffer from type 2 diabetes. What’s more, this number is expected to rise to 852 million by 2050.
Low carb running may prevent and menage type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. As mentioned earlier, train low strategies increase the activity of AMPK. Higher activity of AMPK:
- reduce the amount of insulin produced by the pancreas
- increases the insulin sensitivity of cells
These adaptations can positively affect utilisation of carbohydrates and insulin metabolism. Since excessive sugar intake is one of the contributing factors in the development of type 2 diabetes, reducing sugar consumption may also support prevention and management. However, any changes in diet and lifestyle should always be consulted with doctor and dietician.
Can train low help to lose weight?
Similiary to type 2 diabetes, obseity and excess body fat are more prevalent than every before. People affected by obesity are at a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases or diabetes. In addition to balanced diet , proper sleep and meal timing, low carb running can also support weight loss.
When glycogen is depleted, the body increases rate of fat oxidation. Training in a fasted state ,such as skipping breakfast can accelerate fat loss even faster.
That said, remember to give youself a time. Running with excess body weight put significant stress on joints and muscles.
Injury prevention is way more important than rapid weight loss. Sustainable progress is far more effective—and safer—than extreme shortcuts.
Increased body regeneration
Autophagy is a natural recycling process within cells. Unneccesary or broken cell’s components are broken down into simpler products. It enables cell to produce energy or synthesize new substances.
Autophagy continues uninterrupted with varying intensity depending on the body’s state. Multiple scientific papers have shown that train low startegies increase intensity of autophagy.
Training in fasted state is particulary effective. it combines the effects of fasting and exercise, both of which independently stimulate autophagy. Synergy effect take place so body repairs itself more efficiently than in other train low strategies.
How train low affects body - Summary
Higher Fat Oxidation: Low carbohydrate availability forces the body to use fats for energy. This increases the activity of the enzyme HAD, which is especially beneficial for ultra runners
More Mitochondria: Low glycogen levels activate the key enzyme AMPK, which stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis (the creation of new mitochondria).
Metabolic Disorders: „Train low” strategies may support the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance.
Weight Loss: Running with low carbohydrate availability, especially in a fasted state, can accelerate fat oxidation and support weight loss.
Increased Body Regeneration: Autophagy is a natural cellular recycling process. „Train low” strategies increase the intensity of autophagy.
3. Be carefull with low carb running
Running with high carbohydrate availability is well established among runners and sport scientists. On the opposite end of the spectrum is the train low approach.
Over the past 15 years scientists focus on alternative methods to improve runners endurance.
Most researches agree train low approach is best suited for low-to moderate-intensity workouts. When it comes to high-intensity training, having high carbohydrate availability enables runners to performe longer.

Identical performance outcomes
Current scientific evidence doesn’t show significant performance difference between high and low carbohydrate availibility. Athletes in both groups tend to achieve similar results.
Low carb running won’t help you to run faster or break your personal record. However,it still has a valuable place in endurance training
Greater burden on the body
Train low strategies should be use periodically, not continuously. They place additional stress on the runner’s body ,resulting in improved training adaptation.
In other words your body is better prepared for future challenges. But this additional stress also increases recovery demands—so make sure to allow enough time for regeneration.
Be careful with sleep low
Physical activity is a form of stress for body. Nervous system respond by increasing cortisol level. Level of cortisol is naturally lowest at the evening and highest in the morning.
Sleep low inevitably raises cortisol level in the evening. It can potentially disturb your sleep quality and recovery. If you regularly use the sleep low approach , share with me opinion about your sleep quality.
Be careful with low carb running - Summary
The Train Low approach is best suited for low- to moderate-intensity workouts. For high-intensity training, high carbohydrate availability still allows runners to perform better and longer.
Identical Performance Outcomes: Current scientific evidence shows no significant difference in overall performance between low-carb and high-carb athletes.
Greater Burden on the Body: They place additional stress on the body, which leads to improved adaptation, but also increases recovery demands.
Be Careful with „Sleep Low”: This specific strategy can raise evening cortisol (stress hormone) levels. This may potentially disturb your sleep quality and affect your overall recovery.
4. Conclusion
In an ideal world, there is one solution for everything. However, real life demands tailored approaches for specific goals. That’s exactly how you should think about low carb running.
This approach can be helpfull in some cases but overused it can do more harm than good. Carefully adjust it to your training and enjoy long term benefits.
